Carcinoid cancer is considered rare and not a lot is known as to the treatment for it.
It’s a type of rare cancer that slowly grows in several part of your body.
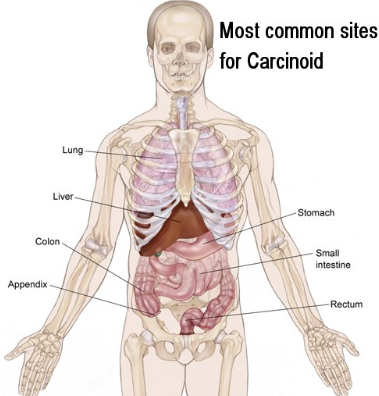
Neuroendocrine is the name of the tumor of this kind which is appears in digestive system.
Symptoms of Carcinoid Cancer
Carcinoid cancer can be in the body for years before showing any symptoms and it is hard to detect in the early stages.
It is only in the later stages that you begin to notice any symptoms and even then many doctors do not know what they are dealing with.
The most common signs and symptoms are:
Tumors in the Digestive System
- Abdominal pain
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Rectal Bleeding and Pain
- Skin flushing and redness, especially in your face and neck
- Diarrhea
If the Carcinoid tumor is in The Lungs
- Difficulty breathing
- Chest Pain
- Wheezing
- Diarrhea
- Skin redness especially in the face and neck
- Weight gain around stomach and upper back
Who’s at Risk for Carcinoid Cancer?
- The elderly’s are at most likely to be diagnosed with carcinoid cancer, however the most common age for such a cancer is around mid 40s and up.
- Women are more likely to be diagnosed with such a cancer than men.
- Genetics and family history of cancer and multiple endocrine neoplasia type I is increasing the chance of getting carcinoid cancer.
- Race. If you are African Americans then you have a higher chance of being diagnose with carcinoid cancer than the whites.
- If you have Anemia you will be at higher risk for carcinoid cancer.
Complications
The cells of carcinoid tumors can secrete hormones and other chemicals, causing a range of complications, including:
- Carcinoid syndrome. Carcinoid syndrome causes redness or a feeling of warmth in your face and neck (skin flushing), chronic diarrhea, and difficulty breathing, among other signs and symptoms.
- Carcinoid heart disease. Carcinoid tumors may secrete hormones that can cause thickening of the lining of heart chambers, valves and blood vessels. This can lead to leaky heart valves and heart failure that may require valve-replacement surgery. Carcinoid heart disease can usually be controlled with medications.
- Cushing’s syndrome. A lung carcinoid tumor can produce an excess of a hormone that can cause your body to produce too much of the hormone cortisol.[note]https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/carcinoid-tumors/symptoms-causes/syc-20351039[/note]
Diagnose of Carcinoid Cancer
This type of cancer usually doesn’t have any symptoms and it is by chance that the doctor will do further examination to make sure with the diagnostic.
- Biopsy to send to the lab to make sure about the certain genes or proteins in order o find the right treatment
- Blood and urine test in order to check for the hormones such as serotonin or 5-HIAA.
- Endoscopy which helps the doctor to see the tumor and it’s usually if the cancer is in stomach or small intestine.
Treatments For Carcinoid cancer
Depending on he location of the tumor and whether cancer been spread to the other organs or not, and age and over all the health of the patient.
- Surgery, in general it’s recommended at the early stage of the cancer and if it’s already spread to other organs surgery is not recommended. Unless, to remove most of the tumor to control the signs and symptoms.
- Medications which can block the cancer cells from hormones caused by the tumor. Also, Medication to boost immune system can help such as Interferon alfa.
- Chemotherapy, to stop cancer cells from growing
- Radiation which is a usage of high X-Rays energy to kill the cancer cells. In most of the times the patient gets the radiation from the outside the body but, sometimes doctor might implant the radioactive seeds inside the body around the tumor.
- Chemoembolization , If Carcinoid tumors spread to the liver:
Treatments for carcinoid tumors that have spread to the liver
Carcinoid tumors commonly spread (metastasize) to the liver. Options for treatment may include:
- Liver surgery. Surgery to remove part of the liver (hepatic resection) may control signs and symptoms caused by liver tumors.
- Stopping blood supply to liver tumors. In a procedure called hepatic artery embolization, a doctor clogs the liver’s main artery (hepatic artery), cutting off the blood supply to cancer cells that have spread to the liver. Healthy liver cells survive by relying on blood from other blood vessels.
- Killing cancer cells with heat or cold. Radiofrequency ablation delivers heat treatments that cause carcinoid tumor cells in the liver to die. Cryoablation uses cycles of freezing and thawing to kill cancer cells.[note]https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/carcinoid-tumors/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20351044[/note]