Many pre-menopausal and postmenopausal women develop uterine fibroids. These are usually benign growths that are made up of connective tissue and smooth muscle.
Fibroids are generated by the thick uterine wall and can vary in size from very small or the size of the head of a pin to the size of a melon.
They can develop in various parts of the uterus.
Uterine fibroids develop mostly during pregnancy and then dissolve after menopause.
So some studies have reasoned that this is why the hormones estrogen and progesterone have a role to play in the growth of fibroids.
Researchers are of the opinion that genetic factors, usually inherited from the paternal side, lead to the development of fibroids.
Also, there are certain abnormalities in some substances called growth factors that lead to fibroid formation.
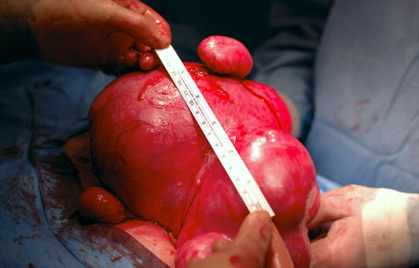
Symptoms of Uterine Fibroids
A fibroid may exist in the uterus without causing any pain or displaying any uterine fibroid symptoms.
But when symptoms do exist, they can manifest as heavy and extended bleeding at the time of menstruation.
1- Bleeding-Fibroid growing in the cavity of the uterus cause this kind of bleeding.
2- Abdominal cramp-like pressure is caused by overly large fibroid, which can also be felt as large lumps and sometimes showing as though the woman is pregnant.
3- Frequency of Urination-There is an increase in the urge and frequency to urinate, especially if a woman is lying down, and sometimes the urine flow is blocked if the fibroid puts pressure on the ureters.
4- Pain During Intercourse-There is a lot of pain during intercourse, and the pressure of fibroid on the rectum can cause constipation.
More about Top Uterine Fibroids Symptoms
Although not s serious problem in more cases, uterine fibroids symptoms should never be ignored.
This problem mainly happens during the years that women can get pregnant and mostly in women who already had one or a few pregnancies. It is not a cancerous illness, and the formed tumors in the uterus are entirely  benign.
Uterine fibroids has some other names including fibromyomas, leiomyomas or myomas.
It has nothing to do with cancer, and they never change to a cancerous condition. So those who have this problem should not be worried about cancer.
The most common uterine fibriods symptoms are:
- The most critical symptom is the continued and prolonged bleeding during the monthly period, which can take more than seven days.
- Feeling pain and pressure in the pelvic area and also inside the pelvis.
- If the tumor is close to the bladder, it can cause problems in urination like feeling pain and difficulty in emptying the bladder.
- When the tumors are significant and can put some pressure on the colon and intestine, it can cause constipation.
- Also, when the tumors apply pressure on some of the nerves on the pelvis area, they can cause pain in the legs and back.

Fibroid tumors become bigger and bigger, and when they make the uterus bigger than usual that the standard stream of blood will not be able to reach and feed it, severe and acute pain comes, and fever will be added to this pain after a while.
Based on the location and position of the tumors, uterine fibroids symptoms can be different from person to person. Tumors that grow toward the inner cavity of uterus are known as Submucosal fibroids. As these tumors affect the inner layer of the uterus, which is the layer involved in monthly periods, they can cause long bleeding periods. Also, as the inner side of the uterus is where the embryo should attach initially and grow, the submucosal fibroids that form inside or close to the inner cavity of uterus are one of the causes of infertility in women.
Unlike submucosal fibroids, subserosal fibroids are the tumors that form in the outer layer of the uterus. Therefore, they have nothing to do with the inside of the uterus, but they can put pressure on the bladder and cause urination problems, and when they are close to clone and rectum, they can cause constipation and also a pain in the back and legs.
Unexplained pain around the pelvis and pelvic area are one of the other uterine fibroids symptoms.
Concerning Fibroids, You should refer to your doctor if.
1. You have problems with urination.
2. You have long and prolonged bleeding during the monthly period of time.
3. You have constipation.
4. You have pain in the pelvis area, or back and legs.
5. You can not get pregnant.
6. You have severe and acute pain in the pelvis area.
Is Uterine Fibroids’ Cancerous?
Fibroid in the uterus is the most common type of tumor found in the reproductive organs of women.
To answer this question, uterine fibroid is generally noncancerous and benign even if their cell shapes are abnormal.
Uterine cancer mostly develops in the uterus lining. But in some sporadic cases, cancer can occur due to some very malignant changes in a fibroid.
Also, if fibroid is growing larger, they do require surgical assessment in order to rule out cancer.
The estimate is that almost 50% of women between the ages of thirty and fifty have a fibroid, although only half that number will experience any symptoms.
What are The Risk Factors of Uterine Fibroid?
Some risk factors have been identified, but research on them is continuing.
If you are exposed to high levels of estrogen, then there is a risk of developing fibroid.
They start growing around puberty but are only likely to be detected or diagnosed when you are an adult.
However, if menstruation has set in early or if you are overweight with a sedentary lifestyle and have never had a child, then you are at risk of developing fibroid.
Some research studies suggest that some combined oral contraceptives containing estrogen and progesterone, as well as hormone replacement therapy that uses these hormones, can lead to fibroid growing.
African-American women are more at risk of developing fibroid because of their diet or other environmental factors.
Hypertension is also linked to an increased risk of fibroid growth.
Main Effects of Fibroid
1- Fibroid can affect fertility and pregnancy and increase the risk of complications during delivery.
2- Anemia is also possible if bleeding due to the fibroid is excessive.
3- If more massive fibroid put pressure on the bladder, then urinary tract infection is likely, sometimes leading to obstruction of the urine flow or damage to the kidneys.
How to Diagnose the Uterus Fibroid?
A pelvic examination will determine the existence of fibroid.
The doctor will require your complete personal and medical history, and diagnosis will also depend on ruling out other conditions with similar symptoms.
A fibroid may not need to be surgically removed if they don’t grow very fast and do not cause pain or too much bleeding.
Monitor your health and have regular pelvic examinations and ultrasounds to keep a watch on the fibroid.
Change your diet and your lifestyle to prevent further growth and complications.
Alternative treatments such as yoga and acupuncture can also help, but take these up after consulting your physician.
When Is It Womb Cancer?
Womb cancer is also called uterine cancer, or endometrial cancer, referring to the inner lining of the womb.
Endometrial cancer is the most common type of womb cancer and develops when the cells of the womb lining begin to proliferate and get out of control.
They can attack all nearby tissues and spread to other parts of the body.
Sometimes these tumors are benign and should not be confused with the malignant type as they could be fibroid and are not cancerous.
These fibroids can cause vaginal bleeding, discharge, and pain, and surgery may then be an option.
Womb cancer is the most common gynecological cancer and usually affects postmenopausal women between the ages of 60 and 74.
It rarely affects younger women Endometriosis adenocarcinoma, papillary serous adenocarcinoma, and clear cell adenocarcinoma are the three most common kinds of endometrial cancer.
Top Risk Factors of Womb Cancer?
Some risk factors are known about endometrial cancer though researchers have not yet established why some women get it and others don’t.
The main factors appear to be age and the amount of estrogen a woman is exposed to in her lifetime, either naturally or from external sources.
So the issues that expose a woman to estrogen include:
- Early menstruation
- Childlessness
- Lack of breastfeeding
- Late menopause
- and nonuser of some contraceptives that stop ovulation
- The race is a factor with white women more likely to be affected than black women.
- Obesity is also a factor to be considered as fat changes other hormones to estrogen and thus increases its levels, making a fat woman more likely to develop endometrial cancer.
However, a high-fat diet is also a cause of this cancer, while a diet that includes phytoestrogens, which are chemicals found in, say, soya, dried fruits, and lignans could ward off womb cancer.
- Diabetes and postmenopausal hormone replacement therapy can also lead to this disease.
- There is also a genetic factor. Some women inherit a mutated gene that causes Lynch syndrome, which can lead to endometrial cancer. If close relatives have developed colon or endometrial cancer, then it’s best to get tested, a very rigorous screening will determine if a woman is at risk and if she is, she can even go in for careful removal of the uterus to avoid the occurrence of cancer.
How to Prevent From Womb Cancer?
Preventive measures against this cancer are not possible because of the screening methods aren’t top notch.
So the best way for a woman to prevent cancer is to have control over such factors as diet, use of contraceptives, and childbearing.
If Lynch Syndrome has been diagnosed, then endometrial biopsies after the age of 35 are a good idea.
What are The Symptoms of Endometrial Cancer?
The symptoms of endometrial cancer manifest with;
- abnormal vaginal bleeding
- Pelvic pain
- Back pain
- Blood in the stool or urine
As these symptoms could indicate other diseases, the physician needs to give you a thorough examination and possibly an ultrasound and a biopsy to determine if it is endometrial cancer.
Surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and hormonal therapy will form the treatment. Make sure you have follow-up visits in case there is a recurrence.